Digital electronics


Digital electronics is a type of electronics. These make use of "boolean logic" and "discrete digital signals" for electronics, devices, and equipment.
Examples of such devices are computers, information appliances, digital cameras, digital televisions, flash memory, key USB memory, mobile phones, hard disks, and devices of computer memory. Digital signal processing works on analog signals after they have been converted to digital form.
Digital circuits
Digital electronics is a branch of electronics concerning digital circuits which apply boolean logic which are represented by electronic logic gates. True and false are represented by different binary values, with 0 volts for true and 5 volts for false. Digital circuits are less vulnerable to electric interference (noise) but consume a lot of energy. Digital circuits were invented in the twentieth century and are the foundation for digital communications and computers.
Digital Electronics Media
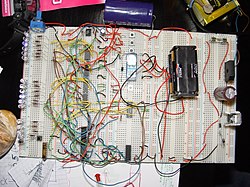
A binary clock, hand-wired on breadboards
Example of a simple circuit with a toggling output. The inverter forms the combinational logic in this circuit, and the register holds the state.
Intel 80486DX2 microprocessor