Fur trade


The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the gain and sale of animal bodies, or parties. It is still a on going tradition. The North American fur trade flourished for 250 years. This long time can be roughly divided into three sections:
- the "French Era" from 1600 to 1760 (See Coureur de bois)
- the "British Era" from 1760 to 1816
- the "American Era" from 1816 to 1850 (See John Jacob Astor)
Before the colonization of the Americas, Russia was a major fur supplier of Western Europe and parts of Asia. The North American fur trade was a central part of the early history of contact in The New World (North America) between European-Americans and Native Americans in the United States and First Nations in Canada.
The North American fur trade flourished for 250 years. This long time can be roughly divided into three sections:
- the "French Era" from 1600 to 1760 (See Coureur de bois)
- the "British Era" from 1760 to 1816
- the "American Era" from 1816 to 1850 (See John Jacob Astor)
One of the earliest companies in the fur trade business was the Hudson's Bay Company, which was created by an English royal charter in 1670. The company still exists today, but now works in the retail business and operates a number of department stores in Canada, the United States and all around the world.[1]
Before the colonization of the Americas, Russia was a major fur supplier of Western Europe and parts of Asia. The North American fur trade was a central part of the early history of contact in The New World (North America) between European-Americans and Native Americans in the United States and First Nations in Canada.
The North American fur trade flourished for 250 years. This long time can be roughly divided into three sections:
- the "French Era" from 1600 to 1760 (See Coureur de bois)
- the "British Era" from 1760 to 1816
- the "American Era" from 1816 to 1850 (See John Jacob Astor)
One of the earliest companies in the fur trade business was the Hudson's Bay Company, which was created by an English royal charter in 1670. The company still exists today, but now works in the retail business and operates a number of department stores in Canada, the United States and all around the world.[1]
Fur Trade Media
A fur shop in Tallinn, Estonia, in 2019
Fur muff manufacturer's 1949 advertisement
Possessions of the city-state of Novgorod c. 1400. Novgorod created a vast territorial empire and controlled much of the fur trade with Europe.
Map of Asia in 1636. With the conquest of Siberia in the 16th and 17th centuries, Russia gained access to the world's richest source of high quality fur.
Cossacks collecting yasak in Siberia
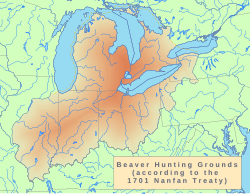
General map of the "Beaver Hunting Grounds" described in "Deed from the Five Nations to the King, of their Beaver Hunting Ground", also known as the Nanfan Treaty of 1701
Rupert's Land, granted as a commercial monopoly to the Hudson's Bay Company in 1670
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Our History". Hudson's Bay Company. Archived from the original on 2017-11-06. Retrieved 2018-03-14.
- Barbara Huck (2000) Exploring the Fur Trade Routes of North America Archived 2008-02-24 at the Wayback Machine (2nd Ed: May 2002)
Other websites
- The Canadian Museum of Civilization - Great Fur Trade Canoes
- A Brief History of the Fur Trade Archived 2006-07-16 at the Wayback Machine
- History of the Fur Trade in Wisconsin Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine
- Museum of the Fur Trade, Chadron, Nebraska USA