GNU Compiler Collection
The GNU Compiler Collection (also known as GCC) is a free software compiler written as part of the GNU project. It originally only compiled C code into machine language, however, now many frontends have been created to allow it to compile other languages.[3][4]
 | |
| Developer(s) | GNU Project |
|---|---|
| Initial release | May 23, 1987[1] |
| Written in | C with some parts written in C++ |
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| Platform | GNU |
| Type | Compiler |
| License | GPLv3+ with GCC Runtime Library Exception[2] |
| Website | gcc |
As well as being the compiler for GNU, it is used by many other projects, most notably many Linux-based operating systems.
Languages
GCC supports compiling the following programming languages:[5]
- C (using the original gcc frontend.)
- C++ (g++ frontend)
- Objective-C
- Objective-C++
- Fortran
- Ada
- Go (gccgo frontend)
GNU Compiler Collection Media
Overview of GCC's extended compilation pipeline, including specialized programs like the preprocessor, assembler and linker.
GCC follows the 3-stage architecture typical of multi-language and multi-CPU compilers. All program trees are converted to a common abstract representation at the "middle end", allowing code optimization and binary code generation facilities to be shared by all languages.
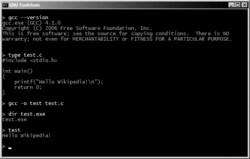
GCC compiling Hello World on Windows
References
- ↑ "GCC Releases". GNU Project. Retrieved July 24, 2020.
- ↑ "GCC Runtime Library Exception". Retrieved July 24, 2020.
- ↑ "GCC Development Mission Statement". Free Software Foundation, Inc. 1999-04-22. Retrieved 2021-01-03.
- ↑ "History - GCC Wiki". gcc.gnu.org. Retrieved 2021-01-03.
- ↑ "GCC Front Ends". Free Software Foundation, Inc. 2020-09-20. Retrieved 2020-01-03.