Khalid ibn al-Walid
Khalid ibn al-Walid (Arabic: خالد ابن الوليد; died 642), also known as Sayf- or Saif Allah ('Sword of God', was a Rashidun military general who led the Muslim conquests of Syria the 7th century.[1]
| Khalid ibn al-Walid خالد ابن الوليد | |
|---|---|
| Born | Medina |
| Died | 642 Medina or Homs |
| Possible burial place | The Khalid ibn al-Walid Mosque, Homs, Syria |
| Allegiance | Quraysh (625–627 or 629) Muhammad (627 or 629–632) Rashidun Caliphate (632–638) |
| Service/branch | Rashidun army |
| Years of service | 629–638 |
| Commands held | |
| Battles/wars |
|
He is famous for his military success, as he commanded the forces of Muhammad and of his immediate successors Abu Bakr and Umar ibn al-Khattab.[1] He won 28 of his confirmed battles[2] against the numerically superior forces of the Byzantine Roman Empire, Sassanid Persian Empire, and their allies. His greatest strategic achievements were his quick conquest of the Persian Empire and conquest of Roman Syria within three years from 633 to 636. His greatest tactical achievements were his successful double envelopment manoeuver at Walaja and his victories at Ullais and Yarmouk.
Khalid Ibn Al-Walid Media
Map showing troop placements and maneuvers of the Battle of Uhud, where Khalid and his horsemen routed a Muslim force led by the Islamic prophet Muhammad in 625
Mount Uhud (pictured in 2009) where the battle took place
The oasis town of Dumat al-Jandal (pictured in 2007). Khalid led an expedition against the city in 630, and may have led another expedition in 633 or 634, though modern historians have cast doubt about the latter campaign or Khalid's role in it.
Map of Khalid's campaigns against the Arab tribes of Najd and the Yamama, both in central Arabia, during the Ridda wars. The itinerary of his campaign is indicated by dashed, red arrows. The territory of the early Muslim state, comprising Mecca, Medina and Ta'if and their environs, is shaded in green
Map of the Yamama region, shaded in red. The region was conquered by Khalid from the Banu Hanifa tribe led by Musaylima
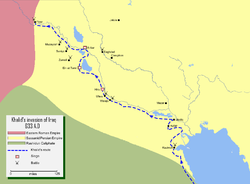
Map detailing Khalid's campaigns in Sasanian Iraq (lower Mesopotamia), based on the general outlines of the Islamic tradition
A map showing three general itineraries of Khalid's march to Syria from Iraq around April 634, as summarized by the historian Fred Donner. The 'desert march' portion of the itineraries are indicated in red.
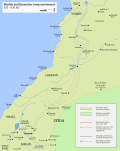
Muslim and Byzantine troop movements in Syria before the battle of Yarmouk in 636.
The ravines of the Yarmouk River, in the vicinity of the Battle of Yarmouk
References
Bibliography
- A.I. Akram, The Sword of Allah: Khalid bin al-Waleed, His Life and Campaigns, Rawalpindi: Nat. Publishing House (1970) ISBN 0-7101-0104-X.
- Lua error in Module:Citation/CS1/Identifiers at line 630: attempt to index field 'known_free_doi_registrants_t' (a nil value).
- Lua error in Module:Citation/CS1/Identifiers at line 630: attempt to index field 'known_free_doi_registrants_t' (a nil value).
- Lua error in Module:Citation/CS1/Identifiers at line 630: attempt to index field 'known_free_doi_registrants_t' (a nil value).
- Lua error in Module:Citation/CS1/Identifiers at line 630: attempt to index field 'known_free_doi_registrants_t' (a nil value).
- Shoufani, Elias; Shufani, Ilyas; Shūfānī, Ilyās; Publishing, Arab Institute for Research and (1973). Al-Riddah and the Muslim Conquest of Arabia. University of Toronto Press. ISBN 978-0-8020-1915-8.
Other websites
- Map of Khalid bin Al-Waleed's Conquests Archived 2007-01-26 at the Wayback Machine