Redox
Reduction
Oxidant + e– ⟶ Product
(Electrons gained; oxidation number decreases)
Oxidation
Reductant ⟶ Product + e–
(Electrons lost; oxidation number increases)

Redox (shorthand for reduction/oxidation) describes all chemical reactions in which atoms have an increase or decrease in oxidation number (oxidation state).[1]
An oxidation number is a number assigned to an element in chemical combination that represents the number of electrons lost (or gained, if the number is negative), by an atom of that element in the compound.
The term redox comes from the two concepts of reduction and oxidation. It can be explained in simple terms:
- Oxidation describes the loss of electrons by a molecule, atom or ion
- Reduction describes the gain of electrons by a molecule, atom or ion
Whether an electron is gained or lost can be easily memorised by the abbreviation OIL RIG, which stands for, "Oxidation Is Loss," or losing electrons, and "Reduction Is Gain," or gaining electrons. Redox reactions can also happen by sharing electrons to form a product by covalent bonding. The term is called redox as neither oxidation or reduction may occur without the other occuring.[2]
In an oxidation reduction reaction, the cation gives an electron to the anion because both ions will have a different charge to attract each other with. In an oxidation reduction reaction, the oxidizing reagent pulls an electron from the other atom to have a net positive charge. The reducing reagent gives an electron to have a net negative charge. However, there are exceptions.[3]
Chemical process
Redox is a chemical process. It can be described in chemical formulas. This example describes the process that occurs in a blast furnace, where iron (Fe) reacts with carbon (C):
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathrm{1) \ C + O_2 \longrightarrow CO_2} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathrm{2) \ CO_2 + C \rightleftharpoons 2 \ CO} }[/math]
- [math]\displaystyle{ \mathrm{3) \ Fe_2O_3 + 3 \ CO \longrightarrow 3 \ CO_2 + 2 \ Fe} }[/math]
- Now elementary iron has been processed.
Redox Media
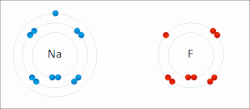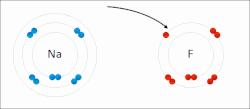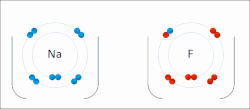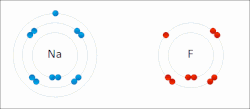
Sodium "gives" one outer electron to fluorine, bonding them to form sodium fluoride. The sodium atom is oxidized, and fluorine is reduced.
When a few drops of glycerol (mild reducing agent) are added to powdered potassium permanganate (strong oxidizing agent), a violent redox reaction accompanied by self-ignition starts.
The international pictogram for oxidizing chemicals
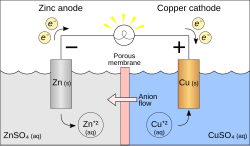
A redox reaction is the force behind an electrochemical cell like the Galvanic cell pictured. The battery is made out of a zinc electrode in a ZnSO4 solution connected with a wire and a porous disk to a copper electrode in a CuSO4 solution.
Oxides, such as iron(III) oxide or rust, which consists of hydrated iron(III) oxides Fe2O3·nH2O and iron(III) oxide-hydroxide (FeO(OH), Fe(OH)3), form when oxygen combines with other elements.
Iron rusting in pyrite cubes
Enzymatic browning is an example of a redox reaction that takes place in most fruits and vegetables.
Related pages
Notes
- ↑ This can be a simple redox process, such as the oxidation of carbon to yield carbon dioxide, the reduction of carbon by hydrogen to yield methane (CH4), or a complex process such as the oxidation of sugar in the human body, through a series of very complex electron transfer processes.
- ↑ Kavanah, Patrick (2018). Chemistry: The Physical Setting. Pearson. ISBN 978-0-328-98858-7.
- ↑ Oxidation and reduction properly refer to a change in oxidation number – the actual transfer of electrons may never occur. Thus, oxidation is better defined as an increase in oxidation number, and reduction as a decrease in oxidation number. In practice, the transfer of electrons will always cause a change in oxidation number, but there are many reactions which are classed as "redox" even though no electron transfer occurs (such as those involving covalent bonds).
Other websites
| The English Wikibooks has more information on: |
- Redox reactions calculator
- Redox reactions at Chemguide
- Online redox reaction equation balancer, balances equations of any half-cell and full reactions