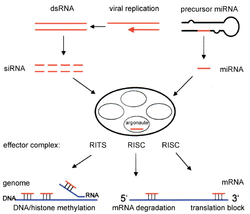
RNA interference
RNA interference (RNAi) is a process in living cells. It adjusts (moderates) the activity of their genes. RNAi molecules are a key to gene regulation. In 2006, Andrew Fire and Craig Mello shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNA interference in the nematode worm Caenorhabditis elegans, published in 1998.
Two types of small RNA molecules – microRNA (miRNA) and small interfering RNA (siRNA) – do the work. These small RNAs bind to normal messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules and increase or decrease their activity. They can prevent a mRNA from producing a protein. RNA interference defends cells against foreign nucleotide sequences – viruses and transposons. Also, they control development, and gene expression in general.
The RNAi pathway is found in many eukaryotes including animals.[1] RNAi is a valuable research tool, in cell culture and in living organisms. Synthetic dsRNA introduced into cells can suppress specific genes of interest. RNAi may be used for large-scale screens that shut down each gene to analyse cellular process or cell division. The pathway is also used as a practical tool in biotechnology and medicine.
Functions
Natural functions
The natural functions of RNA interference are: [2][3]
- Immunity against foreign virus (and other) RNAs
- Upregulation of genes
- Downregulation of genes
Artificial functions
RNA Interference Media
Lentiviral delivery of designed shRNAs and the mechanism of RNA interference in mammalian cells
The stem-loop secondary structure of a pre-microRNA from Brassica oleracea
Left: A full-length Argonaute protein from the archaea species Pyrococcus furiosus. Right: The PIWI domain of an Argonaute protein in complex with double-stranded RNA.
The enzyme Dicer trims double stranded RNA, to form small interfering RNA or microRNA. These processed RNAs are incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which targets messenger RNA to prevent translation.
Illustration of the major differences between plant and animal gene silencing. Natively expressed microRNA or exogenous small interfering RNA is processed by Dicer and integrated into the RISC complex, which mediates gene silencing.
A normal adult Drosophila fly, a common model organism used in RNAi experiments
Example petunia plants in which genes for pigmentation are silenced by RNAi. The left plant is wild-type; the right plants contain transgenes that induce suppression of both transgene and endogenous gene expression, giving rise to the unpigmented white areas of the flower.
References
- ↑ Cerutti H, Casas-Mollano J (2006). "On the origin and functions of RNA-mediated silencing: from protists to man". Curr Genet. 50 (2): 81–99. doi:10.1007/s00294-006-0078-x. PMC 2583075. PMID 16691418.
- ↑ Daneholt, Bertil. "Advanced Information: RNA interference". The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2006. Archived from the original on 2007-01-20. Retrieved 2007-01-25.
- ↑ Bagasra O. & Prilliman K.R. (2004). "RNA interference: the molecular immune system". J. Mol. Histol. 35 (6): 545–53. doi:10.1007/s10735-004-2192-8. PMID 15614608. S2CID 2966105. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2020-03-14. Retrieved 2012-09-13.