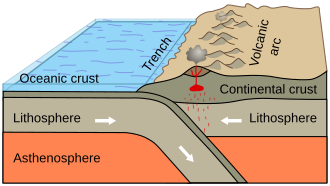
Convergent boundary
A convergent plate boundary is the boundary that occurs when two tectonic plates collide with each other. This causes very large earth movements. Plate collisions can produce earthquakes, volcanoes, the formation of mountains, and other geological events over time.[1] The Himalayas were formed by such a collision. Earthquakes and volcanoes are common near convergent boundaries. This is because of pressure, friction, and plate material melting in the mantle.
The diagram shows some differences between the two types of subduction.
- Oceanic crust moves under. A deep ocean trench forms at the coast, and an arc of mountainous volcanoes forms inland. Seen along the west edge of the Americas.
- Continental crust moves under. The edge of the continental plate folds into a huge mountain range. Behind it is a high plateau. The Himalayas and the Tibetan plateau are a perfect example of this.
Convergent Boundary Media
Map of Earth's principal plates (convergent boundaries shown as blue or mauve lines)
References
- ↑ "Apakah Batas Lempeng Konvergen? · www.greelane.com - Sumber Daya Pendidikan Terbesar di Dunia". www.greelane.com - Sumber Daya Pendidikan Terbesar di Dunia (in Bahasa Indonesia). 2019-07-15. Retrieved 2020-10-10.