Islamic schools and branches
| This article is part of a series on: |
| Islam |
|---|
 |
Islamic schools and branches have different understandings of Islam.
Population of the branches
| Denomination | Population |
|---|---|
| Sunni | Varies: 75% - 90%[1][2] |
| Non-denominational Muslim | 25%[3] |
| Shia | Varies: 10% - 13%[4] |
| Ibadi | 2.7 million[5] |
| Quranism | n/a |
Islamic Schools And Branches Media
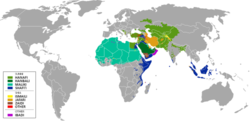
Diagram showing the various branches of Islam: Sunnīsm, Shīʿīsm, Ibadism, Quranism, Non-denominational Muslims, Mahdavia, Ahmadiyya, Nation of Islam, and Sufism.
Related pages
References
- ↑ "Field Listing :: Religions — The World Factbook - Central Intelligence Agency". www.cia.gov. Archived from the original on 2020-03-07. Retrieved 2020-06-12.
- ↑ "Mapping the Global Muslim Population". Pew Research Center. 7 October 2009.
- ↑ "Preface". Pew Research Center's Religion & Public Life Project. 2012-08-09. Retrieved 2020-06-12.
- ↑ "Mapping the Global Muslim Population". Pew Research Center. 7 October 2009.
- ↑ Robert Brenton Betts (2013-07-31). The Sunni-Shi'a Divide: Islam's Internal Divisions and Their Global Consequences. pp. 14–15. ISBN 9781612345222. Retrieved 7 August 2015.
Other websites
| Wikisource has the text of a 1905 New International Encyclopedia article about Islamic schools and branches. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lua error in Module:Commons_link at line 62: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value).. |