Eastern European Summer Time
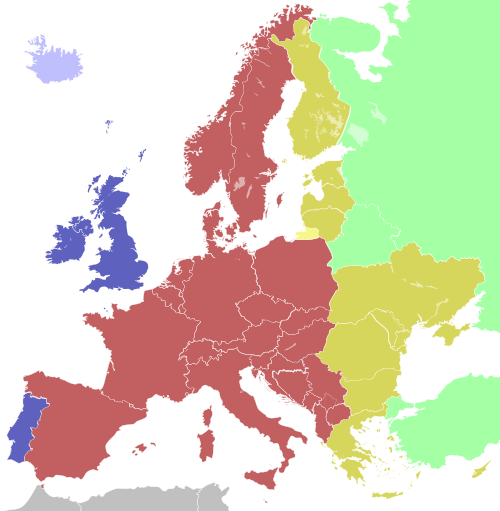
Time zones of Europe in relation to UTC:
Light colours indicate countries that do not observe summer time.
| blue | Western European Time (UTC+0) Western European Summer Time (UTC+1) |
| light blue | Western European Time (UTC+0) |
| red | Central European Time (UTC+1) Central European Summer Time (UTC+2) |
| yellow | Eastern European Time (UTC+2) Eastern European Summer Time (UTC+3) |
| orange | Kaliningrad Time (UTC+3) |
| green | Moscow Time (UTC+4) |
Eastern European Summer Time (EEST) is one of the names of UTC+3 time zone. This zone is 3 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used as a summer daylight saving time in some European, North African, and Middle Eastern countries. During the winter, the Eastern European Time (UTC+2) is used.
Usage
The following countries and territories use Eastern European Summer Time during the summer:
- Belarus, from 1991-2011, now observes Moscow Time all year long
- Bulgaria, regularly since 1979
- Cyprus, regularly since 1979, Northern Cyprus returned to EET on 29 October 2017
- Egypt, used from 1970- 20 April 2011 and again from 16 May 2014- 20 April 2015
- Estonia, in years 1981-88 Moscow Summer Time, regularly EEST since 1989
- Finland, regularly since 1981
- Greece, regularly since 1975
- Israel, regularly since 1948
- Jordan, since 1985
- Latvia, in years 1981-88 Moscow Summer Time, regularly EEST since 1989
- Lebanon, since 1984
- Lithuania, in years 1981-88 Moscow Summer Time, regularly EEST since 1989, in years 1998 was changed to Central European Summer Time, but returned to EEST since 2003
- Moldova, in years 1981-89 Moscow Summer Time, regularly EEST since 1991
- Romania, regularly since 1979
- Russia (Kaliningrad), in years 1981-90 Moscow Summer Time, regularly EEST since 1991
- Syria, since 1983
- Turkey, from 1970-78 and 1985-2016, now observes Turkey Time all year long
- Ukraine, in years 1981-89 Moscow Summer Time, regularly EEST since 1992, but sections of Ukraine including Crimea, Dontesk, and Luhansk have switched to Moscow Time all year long in March 2014.
In 1991 EEST was used also in Moscow and Samara time zones of Russia.
