Biology
Biology is the science that studies life, living things, and the evolution of life. Living things include animals, plants, fungi (such as mushrooms), and microorganisms such as bacteria and archaea.
The term 'biology' is relatively modern. It was introduced in 1799 by a physician, Thomas Beddoes.[1]
People who study biology are called biologists. Biology looks at how animals and other living things behave and work, and what they are like. Biology also studies how organisms react with each other and the environment. It has existed as a science for about 200 years, and before that it was called "natural history". Biology has many research fields and branches. Like all sciences, biology uses the scientific method. This means that biologists must be able to show evidence for their ideas and that other biologists must be able to test the ideas for themselves.
Biology attempts to answer questions such as:
- "What are the characteristics of this living thing?" (comparative anatomy)
- "How do the parts work?" (physiology)
- "How should we group living things?" (classification, taxonomy)
- "What does this living thing do?" (behaviour, growth)
- "How does inheritance work?" (genetics)
- "What is the history of life?" (palaeontology)
- "How do living things relate to their environment?" (ecology)
Modern biology is influenced by evolution, which answers the question: "How has the living world come to be as it is?"
History
The word biology comes from the Greek word βίος (bios), "life", and the suffix -λογία (logia), "study of".[2][3]
Branches
- Algalogy
- Anatomy
- Arachnology
- Bacteriology
- Biochemistry
- Biogeography
- Biophysics
- Botany
- Bryology
- Cell biology
- Cytology
- Dendrology
- Developmental biology
- Ecology
- Endocrinology
- Entomology
- Embryology
- Ethology
- Evolution / Evolutionary biology
- Genetics / Genomics
- Herpetology
- Histology
- Human biology / Anthropology / Primatology
- Ichthyology
- Limnology
- Mammalology
- Marine biology
- Microbiology / Bacteriology
- Molecular biology
- Morphology
- Mycology / Lichenology
- Ornithology
- Palaeontology
- Parasitology
- Phycology
- Phylogenetics
- Physiology
- Taxonomy
- Virology
- Zoology
Biology Media
Diagram of a fly from Robert Hooke's innovative Micrographia, 1665
In 1842, Charles Darwin penned his first sketch of On the Origin of Species.
Model of hydrogen bonds (1) between molecules of water
Organic compounds such as glucose are vital to organisms.
The (a) primary, (b) secondary, (c) tertiary, and (d) quaternary structures of a hemoglobin protein
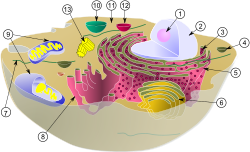
Structure of an animal cell depicting various organelles
Example of an enzyme-catalysed exothermic reaction
Respiration in a eukaryotic cell
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lua error in Module:Commons_link at line 62: attempt to index field 'wikibase' (a nil value).. |
- ↑ "biology, n.". OED Online. 2019. Oxford University Press. Physiology therefore—or more strictly biology—by which I mean the doctrine of the living system in all its states, appears to be the foundation of ethics and pneumatology.
- ↑ "Who coined the term biology?". Info.com. Archived from the original on 2013-05-09.
- ↑ "biology | Origin and meaning of biology by Online Etymology Dictionary". www.etymonline.com. Retrieved 2019-05-29.