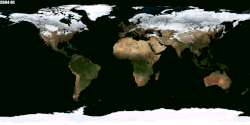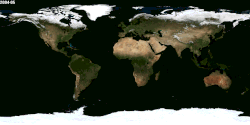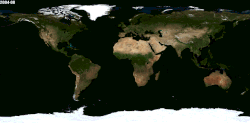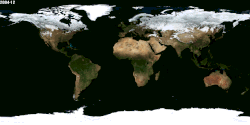
Season
A season is a part of a year. Many areas of the Earth have four seasons in a year: spring, summer, autumn and winter.
Some areas have a different number of seasons. In places which are tropical and subtropical, there are two seasons: the rainy (or wet, or monsoon) season and the dry season. This is because the rain changes more than the temperature. Examples include the tropical parts of Australia (the northern parts of Queensland, Western Australia and the Northern Territory). These are in addition to, or replace the regular season names.[1]
Summer is a warm season because the days are longer and the Sun is high in the sky, giving direct light to the ground. Winter is a cold season because the days are shorter and the Sun is low in the sky, giving indirect light to the ground. Both the changes in the length of the day and the height of the Sun at noon are caused by the axial tilt of the Earth's spin axis with respect to the plane of the Earth's orbit around the Sun. At any time, in any season, the northern and southern hemispheres (halves of the Earth) have opposite seasons.
| Spring | Winter | ||
| The Seasons |
|||
| Summer | Autumn | ||
Dates
Seasons begin and end on different dates in different countries.
The summer solstice is the longest day of the year, and the winter solstice is the shortest. The equinox is the time when the day and the night are the same number of hours, assuming the sun were a point of light at its center. Since civil dawn occurs when the edge of the sun first appears over the horizon and civil dusk occurs when the edge drops over the horizon, the civil length of day is 12 hours long several days prior to the equinoxes.
United States
In the United States, summer begins at summer solstice, winter at winter solstice, spring at the spring (vernal) equinox and autumn at the autumnal equinox.
United Kingdom
In Britain, people traditionally say that the seasons begin about seven weeks earlier: spring begins on Candlemas (February 2), summer on May Day (May 1), autumn on Lammas (August 1), and winter on All Hallows (November 1). These are near the cross-quarter days halfway between the solstices and the equinoxes. The Irish calendar is similar, but Spring begins on February 1.
Denmark
In Denmark, spring begins on March 1, summer on June 1, autumn on September 1 and winter on December 1.
Australia
In Australia, summer begins on December 1, autumn on March 1, winter on June 1, and spring on September 1.
India and Chinese diaspora
In the Chinese calendar and the northern parts of India, the solstices and equinoxes take place in the middle of each season. Summer happens in the hemisphere tilted towards the sun.
High season
High season or tourist season is the time of year that people travel. During high season hotels and resorts increase their prices because demand is higher than in offseason. For example, winter is high season for skiing; summer is high season for beaches. Seasons also affect agriculture; crops are often planted in Spring; harvesting is usually in Autumn.
Season Media
Animation of seasonal differences, notably the snow cover in the Northern Hemisphere
The annual cycle of insolation (Sun energy, shown in blue) with key points for seasons (middle), quarter days (top) and cross-quarter days (bottom) along with months (lower) and Zodiac houses (upper). The cycle of temperature (shown in pink) is delayed by seasonal lag.
Seasonal changes of a tree over a year
Animation of Earth as seen daily from the Sun looking at UTC+02:00, showing the solstice and changing seasons
Related pages
References
- ↑ "Australian weather and the seasons". Australian Government. Archived from the original on 4 November 2015. Retrieved 11 July 2016.
Other websites
- Definition from Dictionary.com
- Names of seasons in various languages from Princeton University
- What causes the seasons?