Ocean
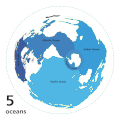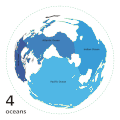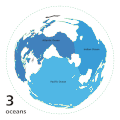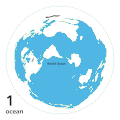
An ocean is a large body of water between continents. Oceans are extremely big and they join smaller seas together. Oceans (or marine) cover 70% of Earth.[1] There are five main oceans: the Pacific Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and the Arctic Ocean.The largest ocean is the Pacific Ocean. The smallest ocean is the Arctic Ocean. Many types of animals live in oceans, such as carp, crabs, starfish, sharks, and whales. Different water movements separate the Southern Ocean from the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. The Southern Ocean is also called the Antarctic Ocean, because it covers the area around Antarctica.
The deepest ocean is the Pacific Ocean. The deep ocean is characterized by cold temperatures, high pressure, and complete darkness. Some very unusual organisms live in this part of the ocean. They do not require high energy from the sun to survive, because they use chemicals from deep inside the Earth.
Color
Although many people believe that the oceans are blue because the water reflects the blue sky, this is actually not true. Water has a very slight blue color that can only be seen when there is a lot of water. However, the main cause of the blue or blue/green color of the oceans is that water absorbs the red part of the incoming light, and reflects the green and blue part of the light. We then see the reflected light as the color of water.
Plants and animals
Many organisms live in oceans. Organisms that live in oceans can live in salt water. They are affected by sunlight, temperature, water pressure, and water movement. Different ocean organisms live near the surface, in shallow waters, and in deep waters. Small plant organisms that live near the surface and use sunlight to produce food are called phytoplankton. Almost all animals in the ocean depend directly or indirectly on these plants. In shallow water, you may find lobsters and crabs. In deeper water, marine animals of many different shapes and sizes swim through the ocean. These include many types of fish, such as tuna, swordfish and marine mammals like dolphins and whales. The skies above the open ocean are home to large sea birds, such as the albatross.[1] In marine reptiles, there is a large number of snakes lived under water, such as Yellow-lipped Sea Krait, Beaked Sea Snake, Belcher’s Sea Snake, Bighead Sea Snake, Black Banded Sea Snake, Brooks Sea Snake, Saint Girons’ Sea Krait and many more.[2]
Harvesting the ocean
Nations like Russia and Japan have lots of huge ships that go to some of the world's best fishing areas for many months. These large ships have libraries, hospitals, schools, repair (fixing) shops and other things that are needed for fishermen and their families.
Many people look at the sea as a source of food, minerals and energy.
Fishing
According to the FishBase.org website, there are 33,200 known fish species, many of which live in the oceans.[3] Many of these fish are a fine source of protein, so many people eat them. Fishing industries is very important because they make jobs and give food to millions of people. Today, usually through ocean fishing, the ocean supplies about 2% of the calories needed by people.[4] Tuna, anchovies, and herring are harvested close to the surface of the ocean.[4] Pollock, flounder, and cod are caught near the ocean floor.[4] More than a million tons of herring are caught every year in the North Pacific and North Atlantic, and almost eight fish out of ten fish are eaten as food for humans. The other fish are used as fertilizer, glue, and pet and other animal food.[4]
Ocean temperatures
There are many different ocean temperatures in the open ocean, both vertically (from top to bottom) and horizontally. Icebergs are made over very cold waters at either pole, while waters at the equator are pretty warm.[4] Water cools and warms more slowly than land does, so land influenced by the ocean has later and milder seasons than land that is farther away from the ocean.
The surface part of the ocean, also called the mixed layer, is not much colder even when we go deeper down.[4] Below this surface zone is a layer of sudden temperature difference, called a thermocline. This is a middle layer hat is from the surface zone down to about 2,600 feet (800 m). Thermoclines may happen only at seasons or permanently, and may change depending on where and how deep it is. As evaporation happens, it begins cooling, and if the water evaporates very quickly, the water becomes saltier. The salty, cold water is denser, so it sinks. This is why warm and cold waters do not easily mix. Most animals and plants live in the warm upper layer. Below the thermocline, the temperature in the deep zone is so cold it is just above freezing - between 32–37.4 °F (0–3 °C).[4]
Ocean Media
Detail of Oceanus attending the wedding of Peleus and Thetis on an Attican black-figure dinos by Sophilos, c. 600–550 BC, British Museum 971.11–1.1.
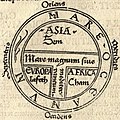
This T and O map, from the first printed version of Isidore's Etymologiae, is surrounded by the MARE OCEANVM (Ocean Sea).
Universalis Cosmographia, also known as the Waldseemüller map, dated 1507, was the first map to show the Americas separating two distinct oceans. South America was generally considered the New World and shows the name "America" for the first time, after Amerigo Vespucci
Bathymetry of the ocean floor showing the continental shelves and oceanic plateaus (red), the mid-ocean ridges (yellow-green) and the abyssal plains (blue to purple) Lighthouse at the coast of Ocean County, New Jersey, U.S., facing the Atlantic Ocean at sunrise
Ocean chlorophyll concentration is a proxy for phytoplankton biomass. In this map, blue colors represent lower chlorophyll and reds represent higher chlorophyll. Satellite-measured chlorophyll is estimated based on ocean color by how green the color of the water appears from space.
The ocean is a major driver of Earth's water cycle.
Movement of water as waves pass
Related pages
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Dinorah Pous (2010). Blue Planet. New York: McGrawHill. p. 117.
- ↑ curie, Marie (2024-09-14). "The Ultimate List of All Sea Snake Species in the World (Stunning Pictures)". SNAKES WORLD. Archived from the original on 2024-09-15. Retrieved 2024-09-15.
- ↑ "FishBase". Archived from the original on 2017-08-23. Retrieved 2015-09-14.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 Sherwin, Frank (2004). The Ocean Book. P.O. Box 726, Green Forest, AR 72638: Master Books. ISBN 0-89051-401-1.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link)