Schengen Area
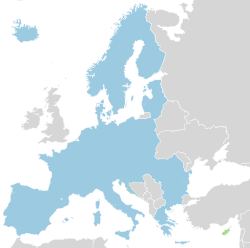
The Schengen Area is an area that includes 29 European countries. All of those countries have signed the Schengen Agreement in Schengen, Luxembourg in 1985.
The Schengen area removes passport control between its member countries. This means travelers who go from one Schengen country to another do not clear immigration checks anymore. Passengers go through immigration checks if they enter or exit the Schengen Area.
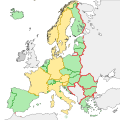
The current members of the Schengen Area are Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Liechtenstein, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden and Switzerland. Because Switzerland is not part of the European Economic Area, customs control in Switzerland still exists.
At this moment, over 420 million people live in the area. The territory covers 4,312,099 square kilometres.
History
On 14 June 1985 the Schengen Agreement was signed. This happened on the boat Princess Marie-Astrid in the middle of the river Moselle. On that place, the borders of France, Germany and Luxembourg meet. Five countries signed the Agreement: Belgium, France, Luxembourg, Netherlands and West Germany. It was signed, but that didn't mean it was already implemented.
In 26 March 1995, all European Union members (except the United Kingdom and Ireland) signed the Agreement. Norway and Iceland also signed the Agreement.
On 1 May 2004, the Czech Republic, Estonia, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Poland, Slovakia, and Slovenia joined the EU. They signed the Schengen agreement on that same day. They implemented the Schengen Agreement on 21 December 2007.
Switzerland joined the Schengen Area on 12 December 2008. Liechtenstein joined it on 19 December 2011. Croatia joined it on 1 January 2023.
Members
Twenty-nine countries belong to the Schengen Area. All these countries are members of the European Union, except Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland.
Current
| Flag | State | Area (km²) |
Population[1] |
Signed or opted in |
Date of first implementation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austria | 83,871 | 8,414,638 | 28 April 1995 | 1 December 1997 | |
| Belgium | 30,528 | 11,007,020 | 14 June 1985 | 26 March 1995 | |
| Bulgaria | 1 January 2007 | 30 March 2024 | |||
| Croatia | 56,594 | 4,213,265 | 9 December 2011 | 1 January 2023 | |
| Czech Republic | 78,866 | 10,535,811 | 1 May 2004 | 21 December 2007b | |
| Denmark (excluding Greenlandd and the Faroe Islandsd) |
43,094 | 5,564,219 | 19 December 1996 | 25 March 2001 | |
| Estonia | 45,226 | 1,340,194 | 1 May 2004 | 21 December 2007b | |
| Finland | 338,145 | 5,391,700 | 19 December 1996 | 25 March 2001 | |
| France (excluding overseas departments and territories) |
674,843 | 65,821,885 | 14 June 1985 | 26 March 1995 | |
| Germany | 357,050 | 81,799,600 | 14 June 1985 | 26 March 1995c | |
| Greece | 131,990 | 10,787,690 | 6 November 1992 | 26 March 2000 | |
| Hungary | 93,030 | 9,979,000 | 1 May 2004 | 21 December 2007b | |
| Icelanda | 103,000 | 318,452 | 19 December 1996 | 25 March 2001 | |
| Italy | 301,318 | 60,681,514 | 27 November 1990 | 26 October 1997 | |
| Latvia | 64,589 | 2,245,357 | 1 May 2004 | 21 December 2007b | |
| Liechtensteina | 160 | 36,010 | 28 February 2008 | 19 December 2011 | |
| Lithuania | 65,303 | 3,207,060 | 1 May 2004 | 21 December 2007b | |
| Luxembourg | 2,586 | 511,840 | 14 June 1985 | 26 March 1995 | |
| File:Flag of Malta.svg | Malta | 316 | 417,608 | 1 May 2004 | 21 December 2007b |
| Netherlands (excluding Aruba, Curaçao, Sint Maarten and the Caribbean Netherlands) |
41,526 | 16,703,700 | 14 June 1985 | 26 March 1995 | |
| Norwaya (excluding SvalbardMayen e) |
385,155 | 4,993,300 | 19 December 1996 | 25 March 2001 | |
| Poland | 312,683 | 38,186,860 | 1 May 2004 | 21 December 2007b | |
| 23x15px | Portugal | 92,391 | 10,647,763 | 25 June 1992 | 26 March 1995 |
| File:Flag of Romania.svg | Romania | 1 January 2007 | 30 March 2024 | ||
| Slovakia | 49,037 | 5,440,078 | 1 May 2004 | 21 December 2007b | |
| Slovenia | 20,273 | 2,048,951 | 1 May 2004 | 21 December 2007b | |
| Spain (excluding Ceuta and Melillaf) |
506,030 | 46,030,109 | 25 June 1992 | 26 March 1995 | |
| Sweden | 449,964 | 9,415,570 | 19 December 1996 | 25 March 2001 | |
| Switzerlanda | 41,285 | 7,866,500 | 26 October 2004 | 12 December 2008 |
a. ^ EFTA states outside the EU that are associated with the Schengen activities of the EU,[2] and where the Schengen rules apply.
b. ^ For overland borders and seaports; since 30 March 2008 also for airports.[3]
c. ^ East Germany became part of the Federal Republic of Germany, joining Schengen, on 3 October 1990. Before this it remained outside the agreement. Despite some media reports, Heligoland is not outside Schengen; it is only outside the European Union Value Added Tax Area.
d. ^ Greenland and the Faroe Islands are not included in the Schengen area, although there might be relaxed checks in the Faroe Islands for flights from Scandinavia, thanks to the Nordic Passport Union, although a passport is still recommended.[4] A Schengen visa issued by a Schengen state will not allow the holder access to either territories, only a Danish visa stamped with either "Valid for the Faroe Islands" or "Valid for Greenland", or both.[5]
e. ^ However, Jan Mayen is part of the Schengen Area.[6]
f. ^ The full Schengen acquis applies to all Spanish territories, but there are border checks on departure from Ceuta and Melilla to Spain or other Schengen countries, because of specific arrangements for visa exemptions for Moroccan nationals resident in the provinces of Tetuan and Nador.[7]
Schengen Visa
Some nationalities need visas to visit the Schengen Area. They only need one Schengen visa for all countries. But they must apply at the embassy of their main destination. The main destination is where a traveller wants to spend the longest time. The visa officer can issue a visa for only one trip or many trips. The officer also decides how long the visa is valid for. The traveller needs to exit before the Schengen visa expires.
Travellers who do not need a Schengen visa can stay for up to 90 days in a 180-day period.
Schengen Area Media
The border checkpoint in La Farga de Moles on the Andorra–Spain border
A Schengen internal border crossing looking into Germany from Austria. There is no border control post. A single common EU-state sign displays the name of the country being entered, in this case Bundes-republik Deutschland (Federal Republic of Germany). The small white sign after the border announces entry into the German state of Bayern (Bavaria).
Temporary border controls conducted by the Danish Police in Kruså at the internal border with Germany
Notes
- ↑ "Eurostat Population Estimate". Eurostat. 1 January 2010. Retrieved 8 January 2010.
- ↑ This terminology is, for example, used in the Final Act of the Agreement concluded by the Council of the European Union and the Republic of Iceland and the Kingdom of Norway concerning the latters' association with the implementation, application and development of the Schengen acquis (OJ L 176,10 July 1999, p. 36).
- ↑ "The final step of Schengen enlargement–controls at internal air borders to be abolished in late March". Slovenia's EU Presidency. 25 March 2008.
- ↑ "At the Gate - FAE - Vága Floghavn". Floghavn.fo. Retrieved 2011-09-15.
- ↑ "General Information on Schengen Short-Term Visas". Royal Danish Embassy in London. 4 June 2009. Archived from the original on 19 April 2010. Retrieved 1 February 2010.
- ↑ Article 14 of the Final Act of the Agreement concluded by the Council of the European Union and the Republic of Iceland and the Kingdom of Norway concerning the latters' association with the implementation, application and development of the Schengen acquis (OJ L 176, 10/07/1999 P. 36) excludes Svalbard from the application of the Schengen rules. As no similar exception was made respecting Jan Mayen, it is part of the Schengen Area.
- ↑ Declaration No. 1. on Ceuta and Melilla attached to the Final Act of the Accession Treaty of the Kingdom of Spain to the Schengen Agreement (OJ L 239, 22.9.2000, p. 69 Archived 2011-05-20 at the Wayback Machine)