Turkish language
Turkish (Türkçe) is a language that is officially spoken in Turkey and Cyprus. Turkish is the 18th most-spoken language in the world.
Turkish is a Turkic language. Turkish is most closely related to other Turkic languages, including Azerbaijani, Turkmen, Uzbek, Kyrgyz, and Kazakh. Another theory is that it is one of the many Altaic languages, which also include Japanese, Mongolian, and Korean.
Mustafa Kemal Atatürk changed the script to the Latin alphabet from the Arabic alphabet. The Turkish government justified the language reform as making Turkish much easier to learn, which would increase literacy. The literacy rate indeed increased greatly after the reform from around 10.5% in 1927[4] to over 90% today. Some say that the move was also to distance the country from the Ottoman Empire, whose documents can no longer be read except by a few scholars.
The Latin alphabet was made to reflect the actual sounds of spoken Turkish, rather than simply transcribing the old Ottoman Arabic alphabet into a new form. The Turkish alphabet has 29 letters, seven of which (Ç, Ğ, I, İ, Ö, Ş, and Ü) have been modified with diacritics for the phonetic requirements of the language. It represents the 20th-century Turkish pronunciation with a high degree of accuracy and specificity. It is the current official alphabet and the latest in a series of distinct alphabets used in different eras.
Simple phrases
- Merhaba = Hello (formal)
- Selam = Hello
- Nasılsın? = How are you?
- Nasılsınız? = How are you? (formal)
- İyiyim = I'm fine
- Teşekkür ederim = Thank you (formal)
- Teşekkürler = Thanks
- Sağ ol = Thank you
- Benim adım ... = My name is ...
- Türkçe bilmiyorum. = I don't speak Turkish.
- İngilizce biliyor musun? = Do you speak English? (informal)
- İngilizce biliyor musunuz? = Do you speak English? (formal)
- Tekrarlar mısın(ız)? = Can you repeat?
- Evet = Yes
- Hayır = No
- Belki = Maybe
- Biraz = A little
- Acıktım. = I'm hungry.
- Dur! = Stop!
- Yapma! = Don't do it!
- İstemiyorum. = I don't want it.
- Tabii = Sure
- Bekledim. = I waited.
- Bana yardım et! = Help me!
Turkish Language Media
The 9th-century Irk Bitig or "Book of Divination"
The 15th century Book of Dede Korkut
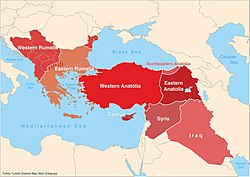
Map of the main subgroups of Turkish dialects across Southeast Europe and the Middle East.
Road sign at the European end of the Bosphorus Bridge in Istanbul.
Atatürk introducing the new Turkish alphabet to the people of Kayseri. September 20, 1928. (Cover of the French L'Illustration magazine)
Artikel 1 der UN Allgemeinen Erklärung der Menschenrechte auf Türkisch
References
- ↑ Taylor & Francis Group (2003). Eastern Europe, Russia and Central Asia 2004. Routledge. p. 114. ISBN 978-1857431872. Retrieved 2008-03-26.
- ↑ "Syrian Turks". Archived from the original on 2009-04-20. Retrieved 2008-09-28.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Turkish at Ethnologue".
- ↑ "Cumhuriyetten sonra kadınların okur yazarlık oranı nedir?"
| This language has its own Wikipedia project. See the Turkish language edition. |