Czechoslovakia
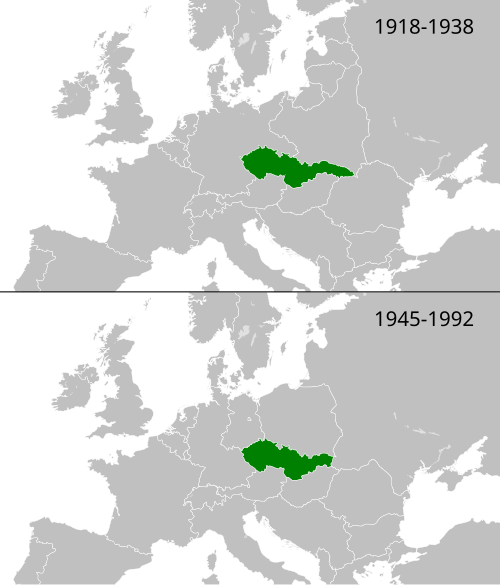
Czechoslovakia, or Czecho-Slovakia,[1] was a country in Europe. It split off from Austria-Hungary in 1918 and split apart in 1993.
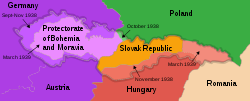
In mid-1938 Nazi Germany took over Czechoslovakia and split off Slovakia. Sudetenland was annexed by Germany, other parts of Czechia became its protectorate named Bohemia and Moravia. After World War II the USSR liberated these lands and kept Zakarpattia because of the Ukrainian (Rusyn) majority in that region.
By 1948 pro-Soviet communists got the power finally and declared the Czechoslovak Socialist Republic. It was a member of Warsaw Treaty Organization and COMECON , one of the richest countries of the Eastern Bloc. In the Prague Spring of the late 1960s, Czechoslovak leader Alexander Dubcek pursued his own policy of a ‘socialism with a human face’. In 1968 Warsaw Pact troops invaded Czechoslovakia to restore the old system.
In 1989 Czechoslovakia peacefully changed its political system in the Velvet Revolution. On 1 January 1993, Czechoslovakia split into the Czech Republic and Slovakia. The countries separated in peace.
Official names
- 1918–1920: Republic of Czechoslovakia (abbreviated RČS)/Czecho-Slovak State,[2] or Czecho-Slovakia/Czechoslovakia
- 1920–1938: Czechoslovak Republic (ČSR), or Czechoslovakia
- 1938–1939: Czecho-Slovak Republic, or Czecho-Slovakia
- 1945–1960: Czechoslovak Republic (ČSR), or Czechoslovakia
- 1960–1990: Czechoslovak Socialist Republic (ČSSR), or Czechoslovakia
- April 1990: Czechoslovak Federative Republic (Czech version) and Czecho-Slovak Federative Republic (Slovak version)
- The country subsequently became the Czech and Slovak Federative Republic, ČSFR, or Československo (Czech version) and Česko-Slovensko (Slovak version).
Czechoslovakia Media
National Anthem of Czechoslovakia
Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk, founder and first president
Czechoslovak declaration of independence rally in Prague on Wenceslas Square, 28 October 1918
A monument to Tomáš Garrigue Masaryk and Milan Štefánik—both key figures in early Czechoslovakia
The partition of Czechoslovakia after Munich Agreement
The car in which Reinhard Heydrich was fatally injured in 1942
Territory of the Second Czechoslovak Republic (1938–1939)
Notes
References
- ↑ "THE COVENANT OF THE LEAGUE OF NATIONS".
- ↑ Votruba, Martin. "Czecho-Slovakia or Czechoslovakia". Slovak Studies Program. University of Pittsburgh. Archived from the original on 15 October 2013. Retrieved 29 March 2009.