Xenon
Xenon is a non-metal chemical element. It has the chemical symbol Xe and atomic number 54. It is one of the few elements that are a gas at the standard temperature and pressure.
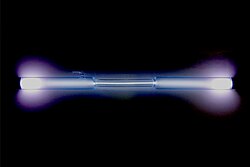
 A xenon-filled discharge tube glowing light blue | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronunciation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | colorless gas, exhibiting a blue glow when placed in an electric field | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard atomic weight (Ar, standard) | 131.293(6)[3] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abundance | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| in the Earth's crust | 2 × 10-9% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| in the solar system | 1.56 × 10-8% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Xenon in the periodic table | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic number (Z) | 54 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Group | group n/a | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Period | period 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Block | [[{{{block}}}-block]] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electron configuration | [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 18, 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phase at STP | Xe: Gas | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point | 161.40 K (−111.75 °C, −169.15 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boiling point | 165.051 K (−108.099 °C, −162.578 °F) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density (at STP) | 5.894 g/L | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| when liquid (at b.p.) | 2.942 g/cm3[4] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Triple point | 161.405 K, 81.77 kPa[5] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Critical point | 289.733 K, 5.842 MPa[5] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of fusion | 2.27 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat of vaporization | 12.64 kJ/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molar heat capacity | 21.01[6] J/(mol·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Vapor pressure
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Oxidation states | 0, +1, +2, +4, +6, +8 (rarely more than 0; a weakly acidic oxide) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electronegativity | Pauling scale: 2.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ionization energies |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Covalent radius | 140±9 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Van der Waals radius | 216 pm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectral lines of xenon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural occurrence | Xe: Primordial | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal structure | face-centered cubic (fcc) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speed of sound | gas: 178 m·s−1 liquid: 1090 m/s | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Thermal conductivity | 5.65×10−3 W/(m·K) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic ordering | diamagnetic[7] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic susceptibility | −43.9×10−6 cm3/mol (298 K)[8] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Number | 7440-63-3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Discovery and first isolation | William Ramsay and Morris Travers (1898) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main isotopes of xenon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
History
Sir William Ramsay and M. W. Travers discovered this element in 1898. The element's name came from the Greek word xenos, which means 'stranger'.
Chemistry
Xenon belongs to the group of the noble gases. Noble gases are very unreactive. However, in 1962, chemists have found that xenon can react with fluorine under special conditions, such as high pressure and high temperature. It is not known why xenon behaves differently under these circumstances. There are also some compounds with oxygen. The gas is not very reactive, because if fulfills the octet rule. This means that a lot of energy is needed to remove an electron from xenon. This activation energy for xenon is 1172 kJ/mol. To remove a second electron from xenon, an energy of 2046.4 kJ/mol is needed.
Known oxidation states of xenon are 0, +1, +2, +4, +6 and +8. However, the most stable form is pure xenon, or the xenon's oxidation state of 0. Xenon has 8 stable isotopes and more than 30 unstable isotopes.
Uses
Xenon gas is used in electron tubes, bactericidal lamps, trobe lamps, and lamps used to excite ruby lasers. It has the atomic mass of 131.294 and is the 5th inert gas in the inner gas group.
Xenon is also a trace gas in the atmosphere, occurring at 87 ±1 nL/L (parts per billion) or approximately 1 in 11.5 million. It is also emitted from some mineral springs.

Xenon Media
Related pages
References
- ↑ Simpson, J. A.; Weiner, E. S. C., eds. (1989). "Xenon". Oxford English Dictionary. Vol. 20 (2nd ed.). Clarendon Press. ISBN 0-19-861232-X.
- ↑ "Xenon". Dictionary.com Unabridged. 2010. Retrieved 2010-05-06.
- ↑ Meija, J.; Coplen, T. B.; Berglund, M.; Brand, W.A.; De Bièvre, P.; Gröning, M.; Holden, N.E.; Irrgeher, J.; Loss, R.D.; Walczyk, T.; Prohaska, T. (2016). "Atomic weights of the elements 2013 (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 88 (3): 265–91. doi:10.1515/pac-2015-0305.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|displayauthors=ignored (|display-authors=suggested) (help) - ↑ "Xenon". Gas Encyclopedia. Air Liquide. 2009.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Haynes, William M., ed. (2011). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. 4.123. ISBN 1439855110.
- ↑ Hwang, Shuen-Cheng; Weltmer, William R. (2000). "Helium Group Gases". Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. Wiley. pp. 343–383. doi:10.1002/0471238961.0701190508230114.a01. ISBN 0-471-23896-1.
- ↑ Magnetic susceptibility of the elements and inorganic compounds, in Lide, D. R., ed. (2005). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (86th ed.). Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0486-5.
- ↑ Weast, Robert (1984). CRC, Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Publishing. pp. E110. ISBN 0-8493-0464-4.
- ↑ Albert, J. B.; Auger, M.; Auty, D. J.; Barbeau, P. S.; Beauchamp, E.; Beck, D.; Belov, V.; Benitez-Medina, C.; Bonatt, J.; Breidenbach, M.; Brunner, T.; Burenkov, A.; Cao, G. F.; Chambers, C.; Chaves, J.; Cleveland, B.; Cook, S.; Craycraft, A.; Daniels, T.; Danilov, M.; Daugherty, S. J.; Davis, C. G.; Davis, J.; Devoe, R.; Delaquis, S.; Dobi, A.; Dolgolenko, A.; Dolinski, M. J.; Dunford, M.; et al. (2014). "Improved measurement of the 2νββ half-life of 136Xe with the EXO-200 detector". Physical Review C. 89. arXiv:1306.6106. Bibcode:2014PhRvC..89a5502A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevC.89.015502.